You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
New to Voyager? Please start here.
Issue Let’s Encrypt certificate using Amazon Route53
This tutorial shows how to issue free SSL certificate from Let’s Encrypt via DNS challenge for domains using Amazon Route53.
This article has been tested with a GKE cluster.
$ kubectl version --short
Client Version: v1.8.8
Server Version: v1.8.8-gke.0
1. Setup Issuer
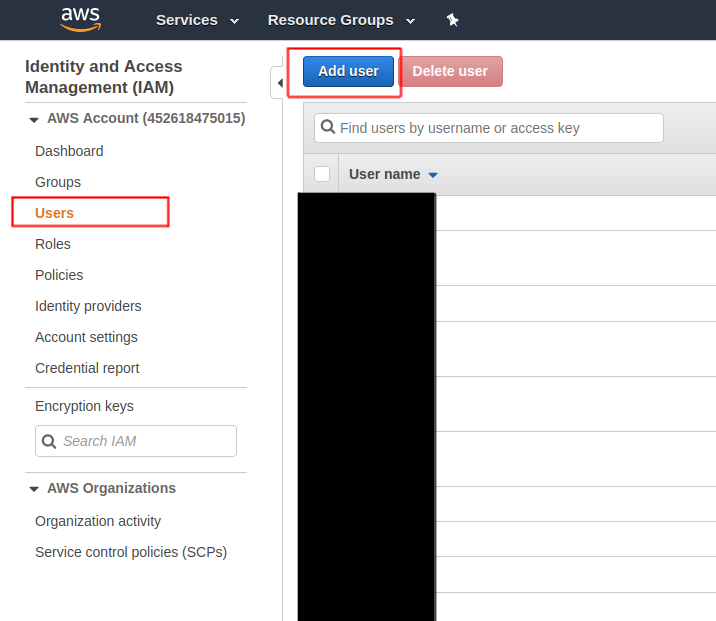
Go to IAM page and create a user
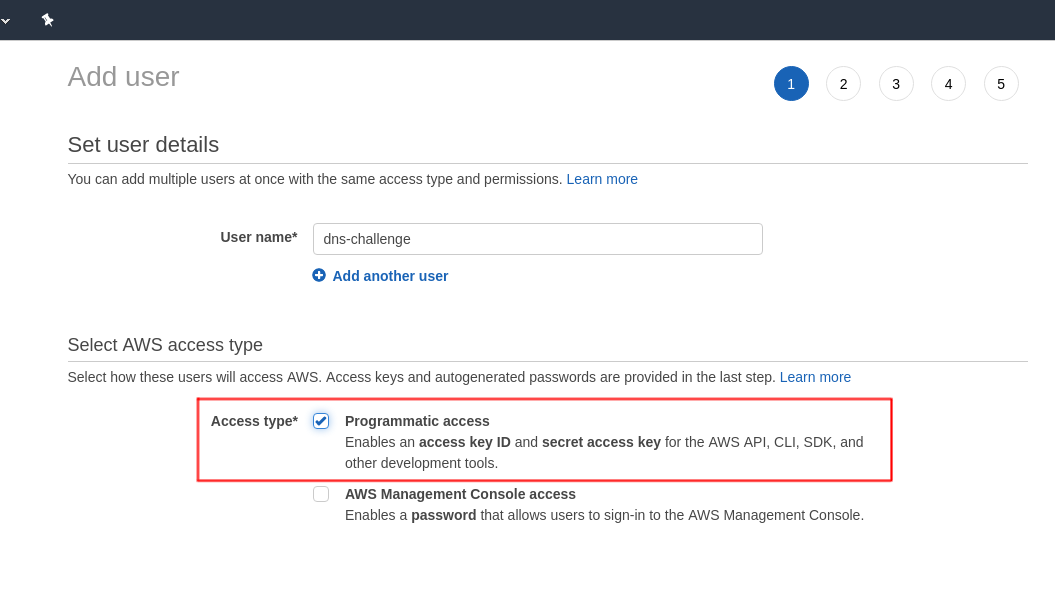
Click on next and select Attach existing policies directly and click on Create Policy. This will take you to a new page.
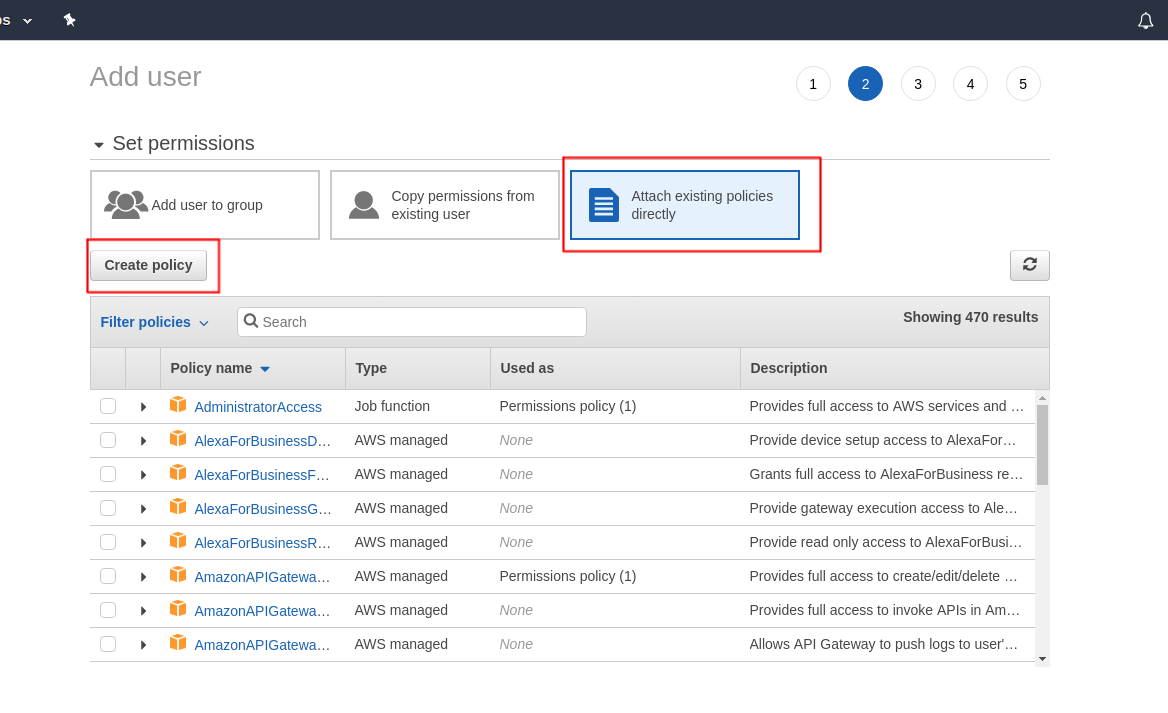
Now click on json and paste this and click Review Policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "route53:GetChange",
"Resource": "arn:aws:route53:::change/*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "route53:ChangeResourceRecordSets",
"Resource": "arn:aws:route53:::hostedzone/*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "route53:ListHostedZonesByName",
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
Name the policy and click Create policy.
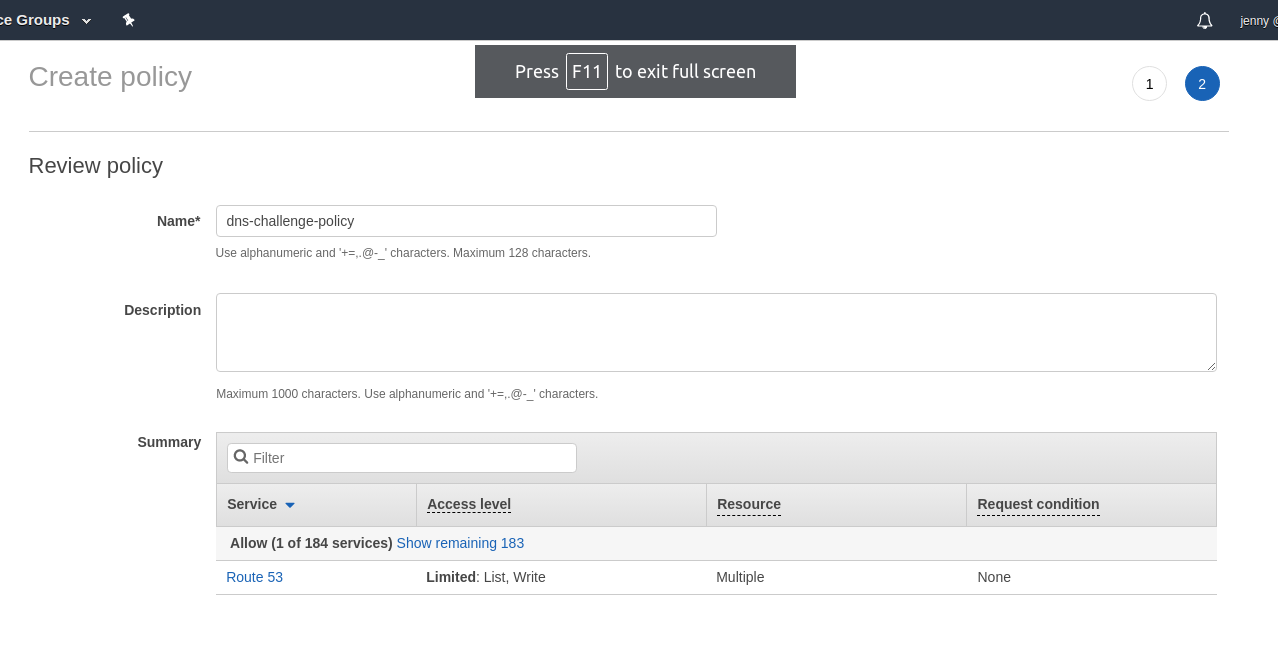
Now go back to previous add user page, hit the refresh button and attach this policy to this user:
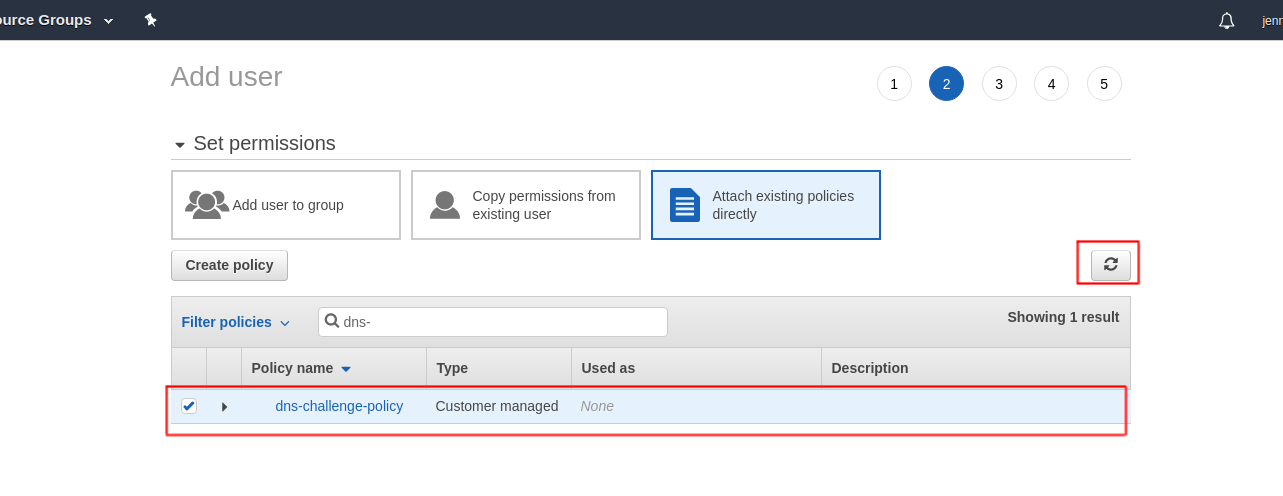
Click on next (tags are optional - you can ignore this) and finish the process. Download the .csv file.
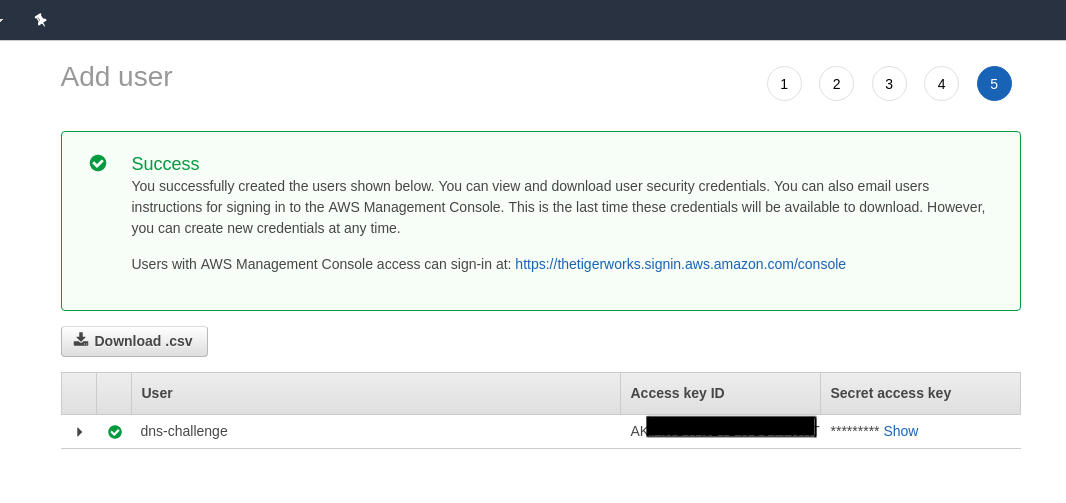
Create a secret with the Secret Access Key
kubectl create secret generic route53-secret --from-literal=secret-access-key="skjdflk4598sf/dkfj490jdfg/dlfjk59lkj"
Copy Access key ID from this same page and hostedZoneID from the following page:
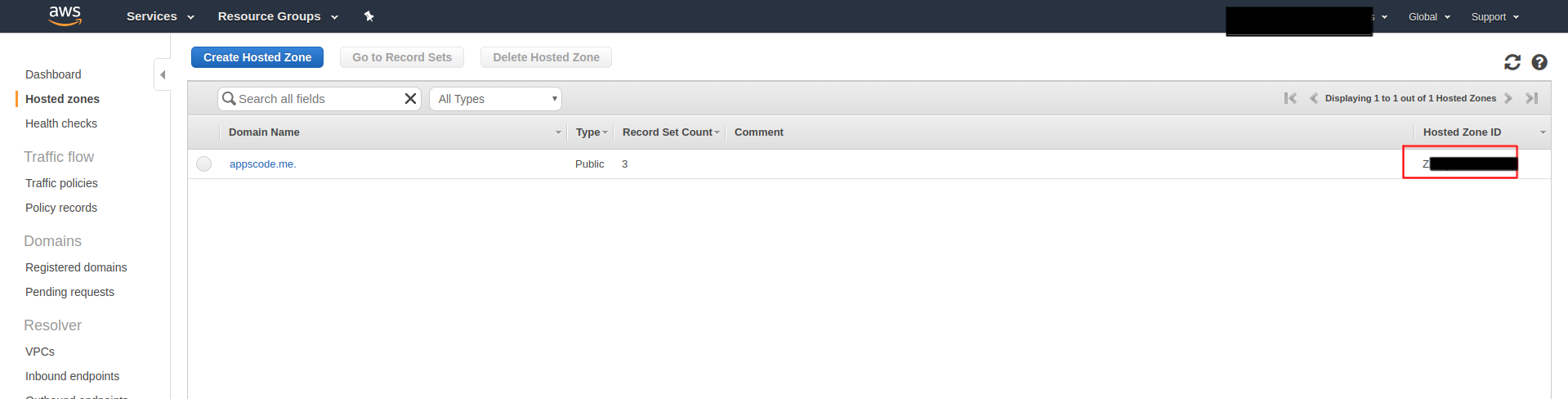
And put them in issuer.yaml
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Issuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt-staging-dns
namespace: default
spec:
acme:
server: https://acme-staging-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
email: [email protected]
# Name of a secret used to store the ACME account private key
privateKeySecretRef:
name: example-issuer-account-key
solvers:
- dns01:
route53:
accessKeyID: KIR2WO5YWT
region: us-east-1
secretAccessKeySecretRef:
name: route53-secret
key: secret-access-key
hostedZoneID: J13B3AB
Then create this issuer by kubectl apply -f issuer.yaml
2. Create Ingress
We are going to use a nginx server as the backend. To deploy nginx server, run the following commands:
kubectl run nginx --image=nginx
kubectl expose deployment nginx --name=web --port=80 --target-port=80
Now create ingress.yaml:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: test-ingress-deploy-k8s-route53-dns
namespace: default
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: voyager
certmanager.k8s.io/issuer: "letsencrypt-staging-dns"
certmanager.k8s.io/acme-challenge-type: dns01
spec:
tls:
- hosts:
- kiteci-route53-dns.appscode.me
secretName: kiteci-route53-dns-tls
rules:
- host: kiteci-route53-dns.appscode.me
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: web
port:
number: 80
path: /
pathType: Prefix
Then take the EXTERNAL-IP from the corresponding service and add a A-record in AWS Route53:
kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
voyager-test-ingress-deploy-k8s-route53-dns LoadBalancer 10.7.248.189 35.225.111.106 443:30713/TCP,80:31137/TCP 21m
3. Create Certificate
Then create this certificate.yaml
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Certificate
metadata:
name: kiteci-route53-dns
namespace: default
spec:
secretName: kiteci-route53-dns-tls
issuerRef:
name: letsencrypt-staging-dns
dnsNames:
- kiteci-route53-dns.appscode.me
List the certificates and describe that certificate and wait until you see Certificate issued successfully when you describe the certificate.
kubectl get certificates.certmanager.k8s.io --all-namespaces
default kiteci-route53-dns True kiteci-route53-dns-tls 1m
kubectl describe certificates.certmanager.k8s.io kiteci-route53-dns
...
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Generated 6s cert-manager Generated new private key
Normal GenerateSelfSigned 6s cert-manager Generated temporary self signed certificate
Normal OrderCreated 6s cert-manager Created Order resource "kiteci-route53-dns-290497833"
Normal OrderComplete 5s cert-manager Order "kiteci-route53-dns-290497833" completed successfully
Normal CertIssued 5s cert-manager Certificate issued successfully
Then visit kiteci-route53-dns.appscode.me from browser and check the certificate that it was issued from let’s encrypt. (For let’s encrypt staging environment, you will see that the certificate was issued by Fake LE Intermediate X1.)










