You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
Install Voyager Enterprise Edition
Voyager Enterprise edition is the open core version of Voyager. Enterprise Edition can be used to manage Voyager custom resources in any Kubernetes namespace. A full features comparison between the Voyager Community edition and Enterprise edition can be found here.
If you are willing to try Voyager Enterprise Edition, you can grab a 30 days trial license from here. To purchase an Enterprise license, please contact us from here.
Get a Trial License
In this section, we are going to show you how you can get a 30 days trial license for Voyager Enterprise edition. You can get a license for your Kubernetes cluster by going through the following steps:
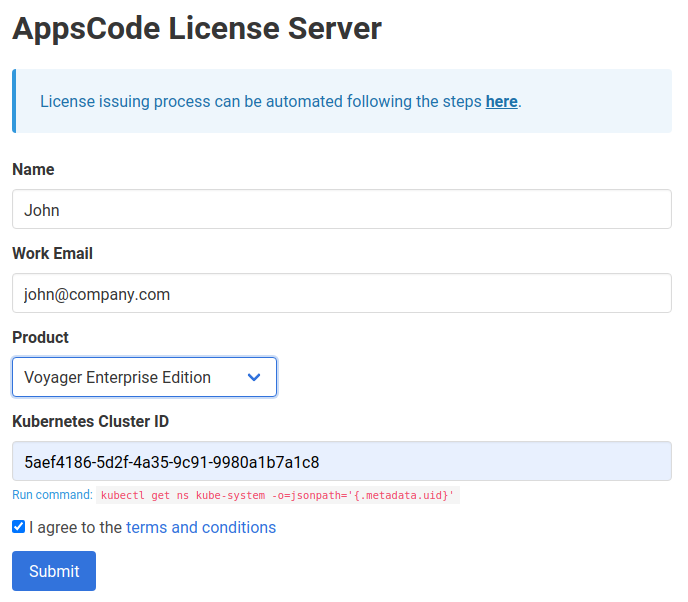
- At first, go to AppsCode License Server and fill up the form. It will ask for your Name, Email, the product you want to install, and your cluster ID (UID of the
kube-systemnamespace). - Provide your name and email address. You must provide your work email address.
- Then, select
Voyager Enterprise Editionin the product field. - Now, provide your cluster ID. You can get your cluster ID easily by running the following command:
kubectl get ns kube-system -o=jsonpath='{.metadata.uid}'
- Then, you have to agree with the terms and conditions. We recommend reading it before checking the box.
- Now, you can submit the form. After you submit the form, the AppsCode License server will send an email to the provided email address with a link to your license file.
- Navigate to the provided link and save the license into a file. Here, we save the license to a
license.txtfile.
Here is a screenshot of the license form.
You can create licenses for as many clusters as you want. You can upgrade your license any time without re-installing Voyager by following the upgrading guide from here.
Voyager licensing process has been designed to work with CI/CD workflow. You can automatically obtain a license from your CI/CD pipeline by following the guide from here.
Get an Enterprise License
If you are interested in purchasing Enterprise license, please contact us via [email protected] for further discussion. You can also set up a meeting via our calendly link.
If you are willing to purchasing Enterprise license but need more time to test in your dev cluster, feel free to contact [email protected]. We will be happy to extend your trial period.
Install
To activate the Enterprise features, you need to install both Voyager Community operator and Enterprise operator chart. These operators can be installed as a Helm chart or simply as Kubernetes manifests. If you have already installed the Community operator, only install the Enterprise operator (step 4 in the following secttion).
Using Helm 3
Voyager can be installed via Helm using the chart from AppsCode Charts Repository. To install, follow the steps below:
$ helm repo add appscode https://charts.appscode.com/stable/
$ helm repo update
$ helm search repo appscode/voyager --version v2022.04.13
NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION
appscode/voyager v2022.04.13 v2022.04.13 Voyager by AppsCode - Secure L7/L4 Ingress Cont...
appscode/voyager-crds v2022.04.13 v2022.04.13 Voyager Custom Resource Definitions
# provider=acs
# provider=aks
# provider=aws
# provider=azure
# provider=baremetal
# provider=gce
# provider=gke
# provider=kind
# provider=openstack
# provider=metallb
# provider=digitalocean
# provider=linode
$ helm install voyager-operator appscode/voyager \
--version v2022.04.13 \
--namespace voyager --create-namespace \
--set cloudProvider=$provider \
--set-file license=/path/to/the/license.txt
To see the detailed configuration options, visit here.
Using YAML
If you prefer to not use Helm, you can generate YAMLs from Voyager chart and deploy using kubectl. Here we are going to show the procedure using Helm 3.
$ helm repo add appscode https://charts.appscode.com/stable/
$ helm repo update
$ helm search repo appscode/voyager --version v2022.04.13
NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION
appscode/voyager v2022.04.13 v2022.04.13 Voyager by AppsCode - Secure L7/L4 Ingress Cont...
appscode/voyager-crds v2022.04.13 v2022.04.13 Voyager Custom Resource Definitions
# provider=acs
# provider=aks
# provider=aws
# provider=azure
# provider=baremetal
# provider=gce
# provider=gke
# provider=kind
# provider=openstack
# provider=metallb
# provider=digitalocean
# provider=linode
$ kubectl create ns voyager
$ helm template voyager-operator appscode/voyager \
--version v2022.04.13 \
--namespace voyager \
--set cloudProvider=$provider \
--set-file license=/path/to/the/license.txt \
--set cleaner.skip=true | kubectl apply -f -
To see the detailed configuration options, visit here.
Verify installation
To check if Voyager operator pods have started, run the following command:
$ kubectl get pods --all-namespaces -l app.kubernetes.io/name=voyager --watch
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
voyager voyager-operator-84d575d55-5lphm 1/1 Running 0 6m42s
Once the operator pods are running, you can cancel the above command by typing Ctrl+C.
Now, to confirm CRD groups have been registered by the operator, run the following command:
$ kubectl get crd -l app.kubernetes.io/name=voyager
Now, you are ready to create your first ingress using Voyager.
Configuring RBAC
Voyager creates an Ingress CRD. Voyager installer will create 2 user facing cluster roles:
| ClusterRole | Aggregates To | Desription |
|---|---|---|
| appscode:voyager:edit | admin, edit | Allows edit access to Voyager CRDs, intended to be granted within a namespace using a RoleBinding. |
| appscode:voyager:view | view | Allows read-only access to Voyager CRDs, intended to be granted within a namespace using a RoleBinding. |
These user facing roles supports ClusterRole Aggregation feature in Kubernetes 1.9 or later clusters.
Using kubectl
Since Voyager uses its own TPR/CRD, you need to use full resource kind to find it with kubectl.
# List all voyager ingress
$ kubectl get ingress.voyager.appscode.com --all-namespaces
# List voyager ingress for a namespace
$ kubectl get ingress.voyager.appscode.com -n <namespace>
# Get Ingress YAML
$ kubectl get ingress.voyager.appscode.com -n <namespace> <ingress-name> -o yaml
# Describe Ingress. Very useful to debug problems.
$ kubectl describe ingress.voyager.appscode.com -n <namespace> <ingress-name>










