You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
New to Voyager? Please start here.
Multiple TLS Certificates
You can secure an Ingress by specifying TLS secrets or certificates.voyager.appscode.com resources inside spec.tls section of the Ingress. Voyager writes the TLS secrets in /etc/ssl/private/haproxy/tls/{secret-name}.pem files inside the HAProxy pod. So if you specify multiple TLS secrets, all of them will be mounted in /etc/ssl/private/haproxy/tls folder. HAProxy presents the certificate to clients which matches with the TLS Server Name Indication (SNI) field of the request. If no SNI is provided by the client or if the SNI does not match with any certificate, then the first loaded certificate will be presented. So you need send request with correct SNI. Note that, Host header does not indicates the SNI.
This tutorial will show you how to configure multiple TLS secrets/certificates for different hosts within a single ingress.
Before You Begin
At first, you need to have a Kubernetes cluster, and the kubectl command-line tool must be configured to communicate with your cluster. Then install Voyager operator in your cluster by following the steps here.
To keep things isolated, we will use a separate namespace called demo throughout this tutorial. Run the following command to prepare your cluster for this tutorial:
$ kubectl create namespace demo
namespace "demo" created
Deploy Test Servers
Deploy a test server that serves two different ports.
$ kubectl apply -f test-server.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: test-server
namespace: demo
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: test-server
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: test-server
spec:
containers:
- name: server
image: appscode/test-server:2.3
imagePullPolicy: Always
env:
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
ports:
- name: http-1
containerPort: 8080
- name: http-2
containerPort: 8989
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: test-server
namespace: demo
labels:
app: test-server
spec:
selector:
app: test-server
ports:
- port: 8080
name: http-1
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8080
- port: 8989
name: http-2
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8989
Create Ingress Without TLS
Create a ingress that points to the different port of the test server for different hosts.
$ kubectl apply -f ingress.yaml
apiVersion: voyager.appscode.com/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: test-ingress
namespace: demo
spec:
rules:
- host: aa.appscode.ninja
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: test-server
servicePort: 8080
- host: bb.appscode.ninja
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: test-server
servicePort: 8989
Configure DNS
Get external IP for the ingress:
$ kubectl get service -n demo
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
test-server ClusterIP 10.55.242.68 <none> 8080/TCP,8989/TCP 6m
voyager-test-ingress LoadBalancer 10.55.249.12 104.154.239.169 80:31584/TCP 1m
Set the external IP of the ingress service to the DNS record for aa.appscode.ninja and bb.appscode.ninja.
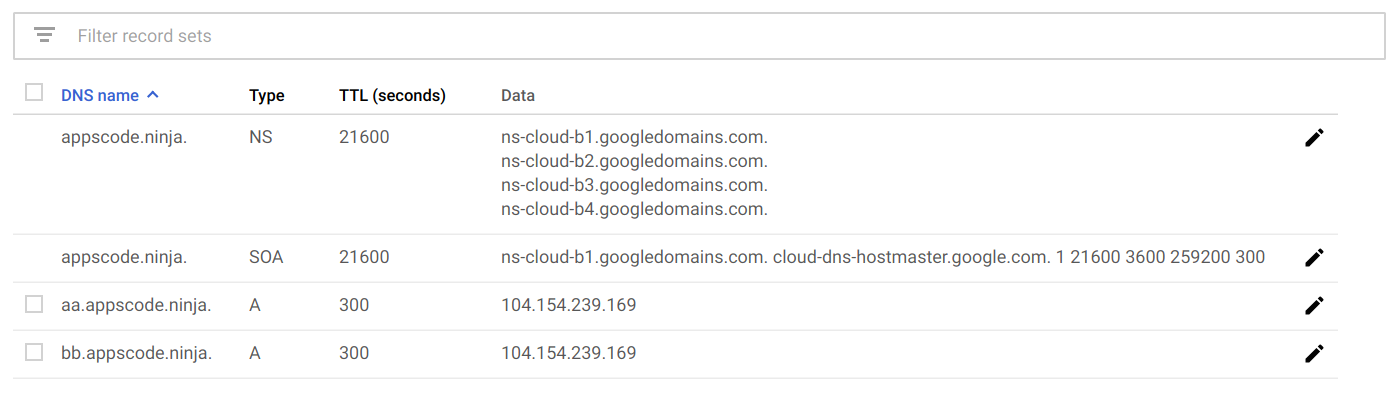
Now wait a little to confirm that these new domains are resolving:
$ dig +short aa.appscode.ninja
104.154.239.169
$ dig +short bb.appscode.ninja
104.154.239.169
Check HTTP Response
Visit http://aa.appscode.ninja and http://bb.appscode.ninja in your browser:
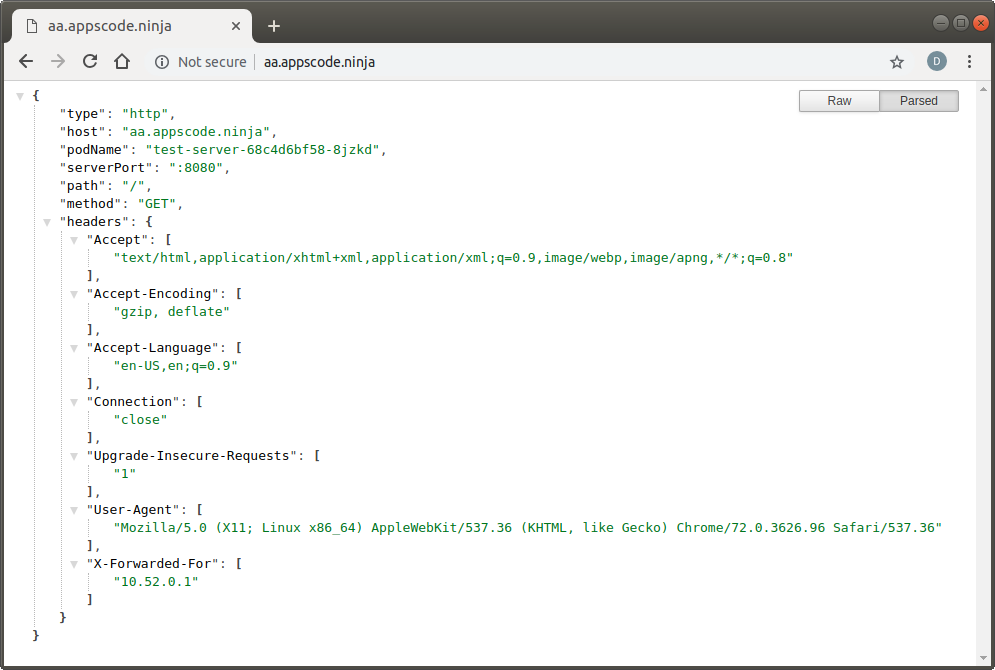
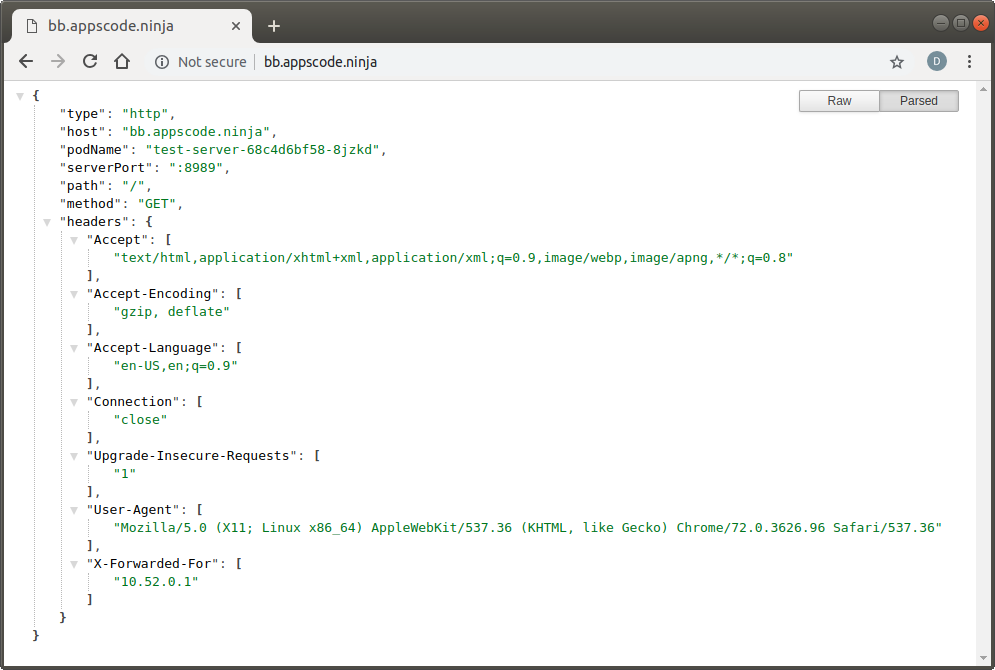
Create Certificate
In this tutorial we will issue free SSL certificates from Let’s Encrypt via DNS challenge for domains using Google Cloud DNS service. If you like to use HTTP challenge or other DNS service provider, please follow the docs here.
Create a secret with Google service account JSON key. Note that, this service account must have DNS Administrator permission.
$ kubectl create secret generic voyager-gce -n demo \
--from-literal=GCE_PROJECT=<project-name> \
--from-file=GOOGLE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_JSON_KEY=<path-to-json-file>
Create another secret to provide ACME user email. Change the email to a valid email address and run the following command:
$ kubectl create secret generic acme-account --from-literal=ACME_EMAIL=[email protected]
-n demo
Create two Certificate CRDs to issue TLS certificates from Let’s Encrypt using DNS challenge:
$ kubectl apply -f certificate.yaml
apiVersion: voyager.appscode.com/v1beta1
kind: Certificate
metadata:
name: aa-ninja
namespace: demo
spec:
domains:
- aa.appscode.ninja
acmeUserSecretName: acme-account
challengeProvider:
dns:
provider: gce
credentialSecretName: voyager-gce
---
apiVersion: voyager.appscode.com/v1beta1
kind: Certificate
metadata:
name: bb-ninja
namespace: demo
spec:
domains:
- bb.appscode.ninja
acmeUserSecretName: acme-account
challengeProvider:
dns:
provider: gce
credentialSecretName: voyager-gce
After several minutes, you should see two new secrets named tls-aa-ninja and tls-bb-ninja. These secrets contains the tls.crt and tls.key.
$ kubectl get secrets -n demo
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
acme-account Opaque 3 2m
default-token-ml4xb kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 1h
tls-aa-ninja kubernetes.io/tls 2 47s
tls-bb-ninja kubernetes.io/tls 2 17s
voyager-gce Opaque 2 2m
voyager-test-ingress-token-8jbgh kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 54m
Ingress With TLS
Update the previously created ingress and specify the certificates in the TLS section.
$ kubectl apply -f ingress-tls.yaml
apiVersion: voyager.appscode.com/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: test-ingress
namespace: demo
spec:
tls:
- hosts:
- aa.appscode.ninja
ref:
kind: Certificate
name: aa-ninja
- hosts:
- bb.appscode.ninja
ref:
kind: Certificate
name: bb-ninja
rules:
- host: aa.appscode.ninja
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: test-server
servicePort: 8080
- host: bb.appscode.ninja
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: test-server
servicePort: 8989
Check HTTPS Response
Visit https://aa.appscode.ninja and https://bb.appscode.ninja in your browser:
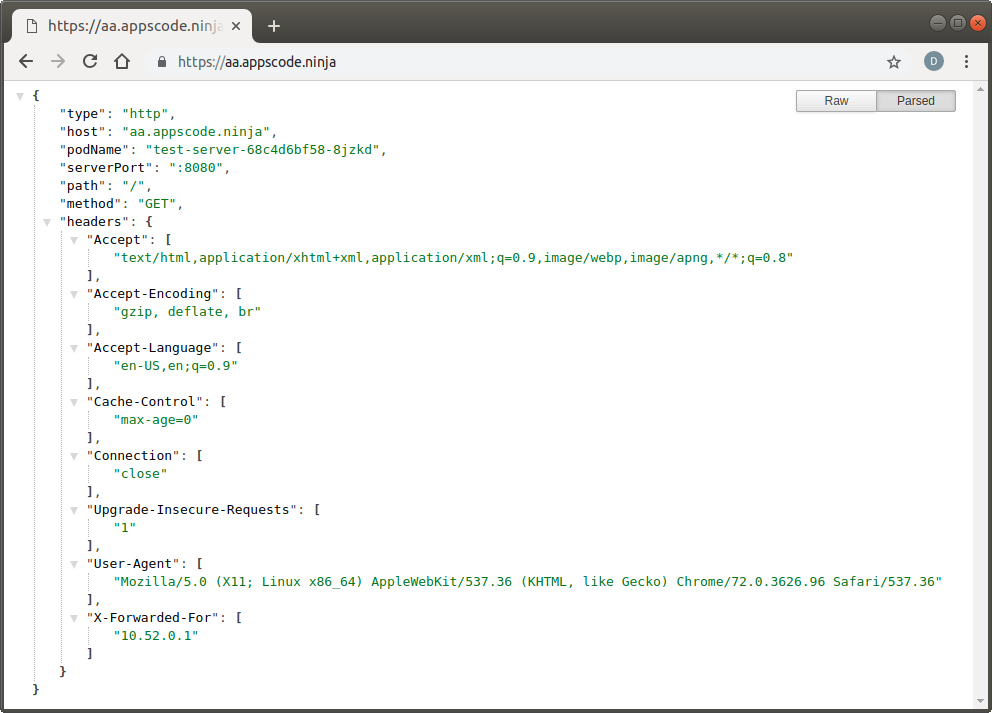
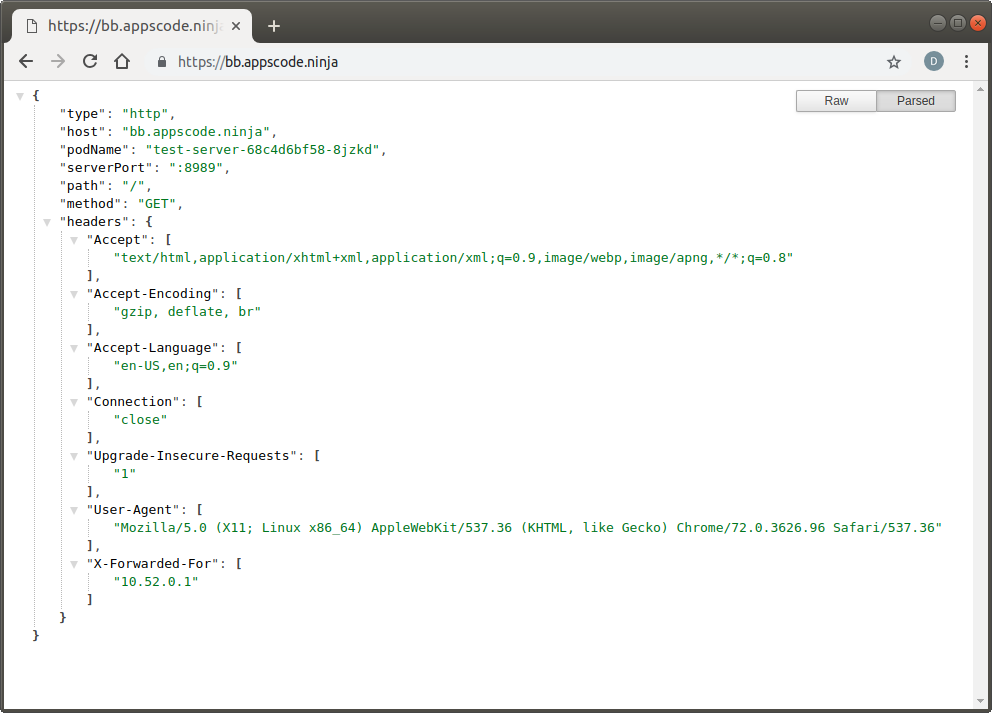
Check Certificate Details
You can see the certificate details from your browser:
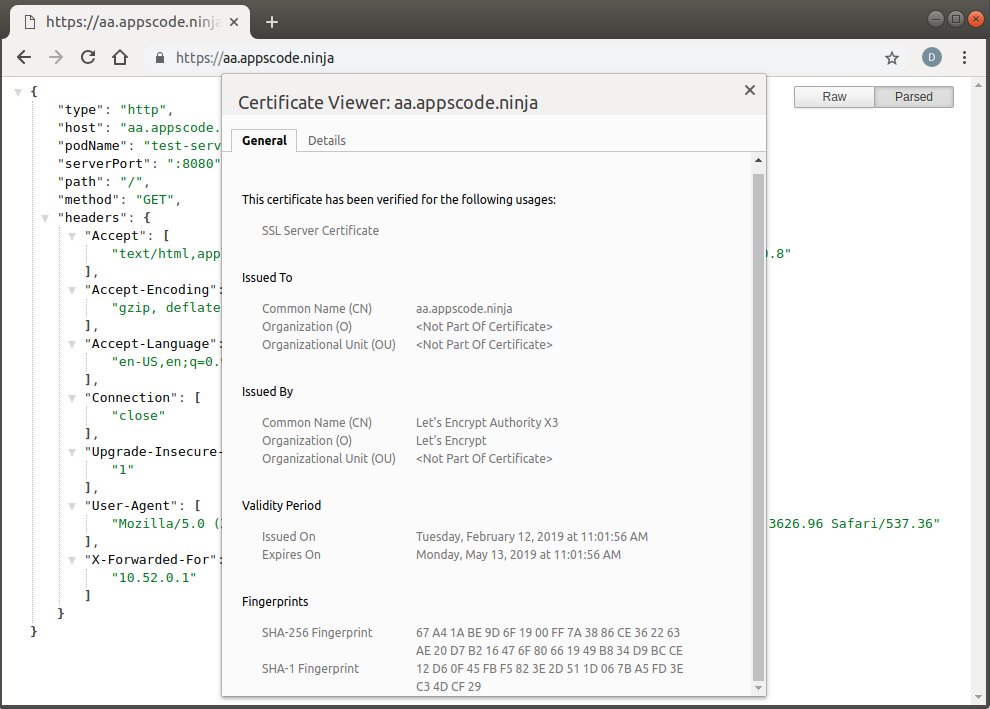
Cleaning up
To cleanup the Kubernetes resources created by this tutorial, run:
$ kubectl delete namespace demo
namespace "demo" deleted
If you would like to uninstall Voyager operator, please follow the steps here.










